Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №6, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Зв’язок рівня глюкози крові, інсуліну та інсулінорезистентності з надмірною масою тіла в пацієнтів із злоякісними новоутвореннями черевної порожнини
Авторы: I.O. Malyshevskyi (1), Yu.M. Myshkovskii (2), O.I. Sydorchuk (3), O.B. Rusak (2), O.Y. Khomko (2), P.V. Kyfiak (2)
(1) - Chernivtsi Regional Clinical Oncology Centre, Chernivtsi, Ukraine
(2) - Bukovinian State Medical University, Chernivtsi, Ukraine
(3) - Bogomolets National Medical University, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
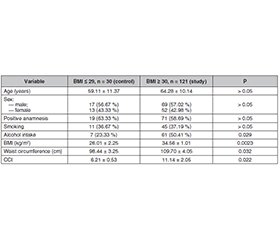
Актуальність. Доведено, що різні типи злоякісних новоутворень можуть бути пов’язані з цукровим діабетом та змінами в метаболізмі вуглеводів. Інші метаболічні порушення, як-от ожиріння, можуть додатково впливати на лікування й подальше спостереження таких хворих. Встановлено багато зв’язків між порушеннями метаболізму та злоякісними новоутвореннями черевної порожнини (ЗНЧП). Вони можуть бути наслідком дещо різних механізмів, причому до 80 % пацієнтів із раком підшлункової залози мали цукровий діабет. Мета: вивчити клінічні й патогенетичні наслідки змін метаболізму глюкози в пацієнтів із злоякісними новоутвореннями черевної порожнини та надмірною масою тіла. Матеріали та методи. Когортне обсерваційне дослідження загалом охоплювало 151 пацієнта зі ЗНЧП, розділених на основну (n = 121, індекс маси тіла (ІМТ) ≥ 30 кг/м2) та контрольну (n = 30, ІМТ ≤ 29 кг/м2) групи. Були проаналізовані діагноз, стадія, поширеність процесу і супутня патологія, низка антропометричних та статистичних параметрів, а також оцінені показники вуглеводного обміну, як-от рівень в крові глюкози, інсуліну й індекс HOMA-IR. Результати. Наявність ЗНЧП суттєво не впливала на концентрацію глюкози в крові. При цьому середнє значення глюкози в досліджуваній групі пацієнтів із надмірною масою тіла було в 1,46 раза (P = 0,014) вищим порівняно з контрольною групою з ІМТ ≤ 29 кг/м2, що свідчить про наявні зміни в метаболізмі вуглеводів. Хоча рівень інсуліну не відрізнявся між групами, індекс HOMA-IR був в 1,57 раза (P = 0,023) вищим в учасників досліджуваної групи. Висновки. Зміни вуглеводного обміну відрізняються в осіб з ожирінням та без нього і можуть розглядатися як важливий клінічний фактор, що потенційно погіршує загальний стан пацієнтів та збільшує ризик післяопераційних ускладнень і незадовільних результатів лікування. Тому цілком доцільно розглянути необхідність консультації ендокринолога в осіб з ожирінням або рутинне включення такого спеціаліста до загальної онкологічної команди.
Background. There is evidence that different types of malignancies may have associations with diabetes mellitus (DM) and changes in carbohydrates metabolism. Other metabolic disorders like obesity may further influence management and patients’ follow-up. There are multiple connections between both metabolism disorders and abdominal malignancies (AM). They may result from slightly different mechanisms with up to 80 % of patients with pancreatic cancer had DM. The purpose was to study the clinical and pathogenetic implications of the glucose metabolism in patients with abdominal malignancies and excessive body weight. Materials and methods. This cohort-based observational study involves a total of 151 patients with AM divided into study (n = 121, body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m2) and control (n = 30, BMI ≤ 29 kg/m2) groups. The diagnosis, staging, prevalence of the process, and concomitant pathology, anthropometric and statistical parameters were analyzed, and carbohydrate metabolism indicators such as blood glucose, insulin and HOMA-IR were assessed. Results. The presence of AM did not significantly influence the blood glucose concentration. The mean value of glucose in study group in patients with excessive body weight was 1.46 times (P = 0.014) higher compared to control group with BMI ≤ 29 kg/m2 depicting present changes in carbohydrates metabolism in these patients. While insulin did not differ between groups, HOMA-IR value was 1.57 times (P = 0.023) higher in study group patients. Conclusions. Changes of carbohydrate metabolism mark the difference between obese and non-obese patients with abdominal malignancies and may be considered an important clinical factor in potentially aggravating the overall condition of the patients and increasing the risk of postoperative complications and treatment failure. Therefore, it is plausible to consider consultation of the specialized endocrinologist in obese AM patients or the routine inclusion of such specialist into the general cancer team.
ожиріння; черевна порожнина; злоякісні новоутворення; хірургія; інсулін; HOMA-IR; глюкоза; цукровий діабет
obesity; abdominal cavity; malignancies; surgery; insulin; HOMA-IR; glucose; diabetes mellitus
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Kozhukhov S, Dovganych N, Smolanka I, Kryachok I, Kova–lyov O. Cancer and war in Ukraine: how the world can help win this battle. JACC CardioOncol. 2022;4(2):279-282. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2022.04.001.
- Siegel RL, Kratzer TB, Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J Clin. 2025;75(1):10-45. doi: 10.3322/caac.21871.
- Wagle NS, Nogueira L, Devasia TP, Mariotto AB, Yabroff KR, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J Clin. 2025;75(4):308-340. doi: 10.3322/caac.70011.
- Jin Q, Liu S, Zhang Y, Ji Y, Wu J, et al. Severe obesity, high inflammation, insulin resistance with risks of all-cause mortality and all-site cancers, and potential modification by healthy lifestyles. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):1472. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85519-9.
- Zhu B, Shen Q. The relationship between diabetes mellitus and cancers and its underlying mechanisms. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.800995.
- Shchubelka K, Wolfsberger WW, Oleksyk O, et al. Genomics of type 1 diabetes in Ukraine initiative. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2025;21(4):343-350. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.21.4.2025.1557.
- Safadi H, Balogh Á, Lám J, Nagy A, Belicza É. Associations between diabetes and cancer: a 10-year national population-based retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024;211:111665. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2024.111665.
- Tsaryk I, Pashkovska N, Pankiv V, Pashkovskyy V, Stankova N. Features of anxiety and depression indicators in patients with autoimmune diabetes mellitus on the background of different vitamin D status. Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 2025;32(2):203-209. doi: 10.46389/rjd-2025-1873.
- Serhiyenko V, Chemerys O, Pankiv V, Serhiyenko A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, cerebral small vessel disease and depressive disorders. International Neurological Journal. 2025;21(3):226-237. doi: 10.22141/2224-0713.21.3.2025.1178.
- Semianiv M, Sydorchuk L, Fedonyuk L, Nebesna Z, Kamyshnyi O, et al. Metabolic and hormonal prognostic markers of essential arterial hypertension considering the genes polymorphism AGTR1 (rs5186) and VDR (rs2228570). Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 2021;28(3):284-291. doi: 10.46389/rjd-2021-1042.
- Wang J, Li D, Ye F, Li J, Qing Z, et al. Global epidemiology of early-onset digestive system malignancy: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;40(6):1525-1535. doi: 10.1111/jgh.17012.
- Pankiv I. Insulin resistance in patients with psoriasis. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2021;17(7):570-574. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.17.7.2021.244973.
- Sydorchuk L, Lytvyn B, Sydorchuk A, Yarynych Y, Daruvuri SP, et al. Alpha-adducin 1 (rs4961) gene and its expression associated with sodium sensitivity in hypertensive patients: a cohort study in the western Ukrainian population. Endocr Regul. 2024;58(1):195-205. doi: 10.2478/enr-2024-0023.
- Pati S, Irfan W, Jameel A, Ahmed S, Shahid RK. Obesity and cancer: a current overview of epidemiology, pathogenesis, outcomes, and management. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(2):485. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020485.
- Semianiv MM, Sydorchuk LP, Dzhuryak VS, Gerush OV, Palamar AO, et al. Association of AGTR1 (rs5186), VDR (rs2228570) genes polymorphism with blood pressure elevation in patients with essential arterial hypertension. J Med Life. 2021;14(6):782-789. doi: 10.25122/jml-2021-0018.
- Hess B, Cahenzli M, Forbes A, Burgos R, Coccolini F, et al.; ESPEN Special Interest Group on Acute Intestinal Failure ESPEN (European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism). Management of acute mesenteric ischaemia: results of a worldwide survey. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023;54:194-205. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.12.022.
- Miranda BCJ, Tustumi F, Nakamura ET, Shimanoe VH, Kikawa D, Waisberg J. Obesity and colorectal cancer: a narrative review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(8):1218. doi: 10.3390/medicina60081218.
- Caturano A, Erul E, Nilo R, Nilo D, Russo V, Rinaldi L, Acierno C, et al. Insulin resistance and cancer: molecular links and clinical perspectives. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025;480(7):3995-4014. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05245-8.
- Màrmol JM, Carlsson M, Raun SH, Grand MK, Sørensen J, et al. Insulin resistance in patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2023;62(4):364-371. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2023.2197124.
- Cobianchi L, Dal Mas F, Massaro M, Biffl W, Catena F, et al.; Team Dynamics Study Group. Diversity and ethics in trauma and acute care surgery teams: results from an international survey. World J Emerg Surg. 2022;17(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13017-022-00446-8.
- De Simone B, Ansaloni L, Sartelli M, Kluger Y, Abu-Zidan FM, et al.; OBA trial supporters; Catena F. The operative mana–gement in bariatric acute abdomen (OBA) survey: long-term complications of bariatric surgery and the emergency surgeon’s point of view. World J Emerg Surg. 2020;15(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0281-y.
- Li M, Chi X, Wang Y, Setrerrahmane S, Xie W, Xu H. Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):216. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01073-0.
- Aune D, Sen A, Prasad M, Norat T, Janszky I, et al. BMI and all cause mortality: systematic review and non-linear dose-response meta-analysis of 230 cohort studies with 3.74 million deaths among 30.3 million participants. BMJ. 2016;353:i2156. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i2156.
- Reichert M, Sartelli M, Weigand MA, Hecker M, Oppelt PU, et al.; WSES COVID-19 emergency surgery survey collaboration group. Two years later: is the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic still having an impact on emergency surgery? An international cross-sectional survey among WSES members. World J Emerg Surg. 2022;17(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13017-022-00424-0.
- Ohkuma T, Peters SAE, Woodward M. Sex differences in the association between diabetes and cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 121 cohorts including 20 million individuals and one million events. Diabetologia. 2018;61(10):2140-2154. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4664-5.
- Lohi P, Auvinen A, Niskanen L, Partonen T, Haukka J. Does the duration of diabetes increase the risk of cancer? A nationwide population-based cohort of patients with new-onset diabetes and a matched reference cohort. Int J Cancer. 2024;154(11):1940-1947. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34858.
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119.