Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 20, №6, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Гастроезофагеальна рефлюксна хвороба у дітей та підлітків: мультифакторна модель патогенезу, клінічні особливості, фактори ризику та сучасні стратегії ведення
Авторы: Бекетова Г.В., Горячева І.П., Солдатова О.В., Шарікадзе О.В.
Національний університет охорони здоров’я імені П.Л. Шупика, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
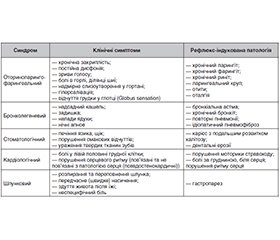
Актуальність. Гастроезофагеальна рефлюксна хвороба у дітей та підлітків є актуальною проблемою педіатричної гастроентерології, що характеризується зростанням її поширеності, варіативністю клінічних проявів та діагностичними труднощами, зумовленими віковими особливостями пацієнтів. Метою роботи було здійснення огляду сучасних наукових досліджень щодо поширеності та особливостей клінічного перебігу захворювання у дітей та підлітків, впливу факторів ризику та основних патофізіологічних механізмів на його формування, підходів до діагностики та лікування. Матеріали та методи. Огляд літературних джерел базувався на аналізі результатів опублікованих у відкритому доступі наукових досліджень з використанням інформаційно-пошукових систем PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar та ResearchGate щодо гастроезофагеальної рефлюксної хвороби, факторів ризику та патогенетичних механізмів її формування, підходів до лікування. Ми розглядали наукові дослідження, опубліковані переважно за останні 5 років. Для статті відібрано 96 наукових публікацій. Результати. У статті висвітлено інформацію щодо мультифакторної природи захворювання, його зв’язку з ожирінням, особливостями харчування, психоемоційними розладами та змінами мікробіому травного тракту у пацієнтів. Окрему увагу приділено специфіці клінічних проявів хвороби, її стравохідним та позастравохідним симптомам та сучасному діагностичному алгоритму, що передбачає ретельний збір анамнезу, аналіз клінічних симптомів і результатів використання інструментальних методів дослідження. Розглянуто актуальні немедикаментозні та фармакологічні підходи до терапії захворювання, підкреслено важливість міждисциплінарного підходу з урахуванням психологічного та метаболічного статусу пацієнта для запобігання розвитку ускладнень та підвищення ефективності терапії. Висновки. Подальші дослідження мають спрямовуватись на уточнення ролі порушень мікробіому, метаболічних і психоемоційних факторів у формуванні та прогресуванні гастроезофагеальної рефлюксної хвороби у дітей та підлітків для оптимізації лікувальних стратегій, зменшення ризиків формування ускладнень та поліпшення якості життя.
Background. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in children and adolescents is a relevant issue in modern pediatric gastroenterology, characterized by increasing prevalence, variability of clinical manifestations, and diagnostic challenges due to age-specific features of patients. The purpose was to summarize current data on the prevalence and characteristics of the clinical course in children and adolescents, influence of risk factors and the main pathophysiological mechanisms on its formation, approaches to diagnosis and treatment. Materials and methods. The literature review was based on the analysis of the results of published open access scientific studies using the information search systems PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar and ResearchGate on gastroesophageal reflux disease, risk factors and pathogenetic mechanisms of its formation, treatment approaches. We mainly considered studies published within the last five years. A total of 96 articles were included for analysis. Results. Gastroesophageal reflux disease has a multifactorial nature and is associated with obesity, dietary habits, psycho-emotional disorders, and alterations in the gastrointestinal microbiome. Special attention is paid to the specificity of the clinical manifestations of the disease, its esophageal and extraesophageal symptoms and the modern diagnostic algorithm, which involves comprehensive evaluation of medical history, analysis of clinical features and results of using instrumental research methods. Current non-drug and pharmacological interventions to the therapy of the disease are considered; the importance of an interdisciplinary approach taking into account the psychological and metabolic status of a patient to prevent the development of complications and increase the effectiveness of therapy is emphasized. Conclusions. Further research should be directed at clarifying the role of microbiome disturbances, metabolic, and psycho-emotional factors in the development and progression of gastroesophageal reflux disease in children and adolescents, with the aim of optimizing treatment strategies, minimizing complications, and enhancing quality of life.
діти; підлітки; харчування; здоровий спосіб життя; гастроезофагеальна рефлюксна хвороба; ожиріння; тривожність; патогенез; діагностика; лікування; огляд
children; adolescents; nutrition; healthy lifestyle; gastroesophageal reflux disease; obesity; anxiety; pathogenesis; diagnostics; treatment; review
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Thejavath AS, Rajender A, Shriram C. Assessment of Gastroesopha–eal Reflux Disease (GERD) Symptoms and Associated Lifestyle Factors Among Young Adults: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study. European Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine. 2024;14(4):1153-1156. doi: 10.5083/ejcm/2024.
- Beketova HV, Moshchych ОО, Pogorielova KH, Kobylynska LI. Retrospective analysis of the frequency and characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux disease in children for 20 years. Сhild’s health. 2025;20(2):107-116. doi: 10.22141/2224-0551.20.2.2025.1800.
- Azer SA, Goosenberg E. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) [Updated 2025 Jul 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554462/.
- Marabotto E, Savarino V, Ghisa M, et al. Advancements in the use of 24-hour impedance-pH monitoring for GERD diagnosis. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022;65:102264. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102264.
- Zhang D, Stein R, Lu Y, et al. Pediatric Gastrointestinal Outcomes During the Post-Acute Phase of COVID-19: Findings from RECOVER Initiative from 29 Hospitals in the US. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 9:2024.05.21.24307699. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.21.24307699. PMID: 38826331; PMCID: PMC11142297.
- Zheng Z, Shang Y, Wang N, et al. Current Advancement on the Dynamic Mechanism of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. International Journal of Biological Sciences. 2021;17(15):4154-4164. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.65066.
- Наказ Міністерства охорони здоров’я України від 29.06.2023 р. № 1179 «Про затвердження Стандарту медичної допомоги «Гастроезофагеальна рефлюксна хвороба у дітей».
- Sandipan S, Sudipta M. Pediatric Obesity and Non-Hepatobiliary Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Comprehensive Review. Gastroint Hepatol Dig Dis. 2024;7(4):1-8.
- Singendonk M, Goudswaard E, Langendam M, et al. Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Symptoms in Infants and Children: A Systematic Review. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019 Jun;68(6):811-817. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002280. PMID: 31124988.
- Kesavelu D, Franklyn N, Venkatraghavan C, Narayan D, Ravindra PK, Wasim A. Prevalence and Severity of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Indian Children Presenting with Symptoms of Acid Reflux: A Real-world Evidence Study. Turk Arch Pediatr. 2025 Jan 27;60(3):341-343. doi: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2025.24140. PMID: 39873348; –PMCID: PMC12093388.
- Sintusek P, Mutalib M, Thapar N. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in children: What’s new right now? World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Mar 16;15(3):84-102. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v15.i3.84. PMID: 37034973; PMCID: PMC10080553.
- Puri NB, Sanchez R. Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children. Curr Treat Options Peds. 2025;(11):10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40746-024-00321-5.
- Leung AK, Hon KL. Gastroesophageal reflux in children: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2019 Jun 17;8:212591. doi: 10.7573/dic.212591. PMID: 31258618; PMCID: PMC6586172.
- Eman FB, Sudarshan J. The enigma of gastroesophageal reflux disease among convalescing infants in the NICU: It is time to rethink. International Journal of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 2020;7(1):28-32. ISSN 2352-6467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpam.2020.03.001.
- Britt Frisk Pados, Emma S. Davitt Pathophysiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Nonpharmacologic Strategies for Symptom Management. Nursing for Women’s Health. 2020;24(2):101-114. ISSN 1751-4851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nwh.2020.01.005.
- Ma J, Li Z, Zhang W, et al. Comparison of gut microbiota in exclusively breast-fed and formula-fed babies: a study of 91 term infants. Sci Rep. 2020;10:15792. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72635-x.
- Vanessa ZY McLoughlin, Noor HA Suaini, Kewin Siah, et al. Prevalence, risk factors and parental perceptions of gastroesopha–geal reflux disease in Asian infants in Singapore. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2022;51:263-71. https://doi.org/10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.2021411.
- Francis D, Chawla A, LaComb JF, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux and PPI exposure alter gut microbiota in very young infants. Front Pediatr. 2023 Oct 31;11:1254329. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1254329.
- Vandenplas Y, Orsi M, Benninga M, Gatcheco F, Rosen R, Thomson M. Infant gastroesophagealreflux disease management consensus. Acta Paediatr. 2024;113:403-410. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.17074.
- Rosen R, Vandenplas Y, Singendonk M, et al. Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepato–logy, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Mar;66(3):516-554. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001889. PMID: 29470322; PMCID: PMC5958910.
- Soderborg TK, Carpenter CM, Janssen RC, Weir TL, Robertson CE, Ir D, et al. Gestational diabetes is uniquely associated with altered early seeding of the infant gut microbiota. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:603021. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.603021.
- Princisval L, Rebelo F, Williams BL, Coimbra AC, Crovesy L, Ferreira AL, et al. Association between the mode of delivery and infant gut Microbiota composition up to 6 months of age: a systematic literature review considering the role of breastfeeding. Nutr Rev. 2021;80:113-27. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuab008.
- Patrick DM, Sbihi H, Dai DLY, Al Mamun A, Rasali D, Rose C, et al. Decreasing antibiotic use, the gut microbiota, and asthma incidence in children: evidence from population-based and prospective cohort studies. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:1094-105. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30052-7.
- Dahlen HG, Foster JP, Psaila K, et al. Gastro-oesophageal reflux: a mixed methods study of infants admitted to hospital in the first 12 months following birth in NSW (2000-2011). BMC Pediatr. 2018 Feb 12;18(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12887-018-0999-9. PMID: 29429411; –PMCID: PMC5808415.
- Curien-Chotard M, Jantchou P. Natural history of gastroeso–phageal reflux in infancy: new data from a prospective cohort. BMC Pediatr. 2020 Apr 7;20(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-02047-3. PMID: 32264869; PMCID: PMC7137340.
- Visnes ES, Hallan A, Bomme M, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms among adolescents, the HUNT study. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. 2024:59(7):816-820. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365521.2024.2349646.
- Fernández-González SM, Moreno-Álvarez A, Solar-Boga A. Proton Pump Inhibitors in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Children (Basel). 2024 Mar 1;11(3):296. doi: 10.3390/children11030296. PMID: 38539331; PMCID: PMC10969042.
- Nirwan JS, Hasan SS, Babar ZUD, et al. Global Prevalence and Risk Factors of Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD): Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5814. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62795-1.
- Sadafi S, Azizi A, Pasdar Y, Shakiba E, Darbandi M. Risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a population-based study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 5;24(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03143-9. PMID: 38317085; PMCID: PMC10840240.
- Chuting Yu, Tinglu Wang, Ye Gao, et al. Association between physical activity and risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A syste–matic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2024;13(5):687-698, ISSN 2095-2546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2024.03.007.
- Abu El Haija M, Agostoni C. Children With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Consume More Calories and Fat Than Controls. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020 Jun;70(6):761-762. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002656. PMID: 32443028.
- Borodina G, Morozov S. Children With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Consume More Calories and Fat Compared to Controls of Same Weight and Age. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020 Jun;70(6):808-814. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002652. PMID: 32443037.
- Xie M, Deng L, Fass R, Song G. Obesity is associated with higher prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease and reflux related complications: A global healthcare database study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024 Apr;36(4):e14750. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14750. Epub 2024 Jan 31. PMID: 38297487.
- Andrásdi Z, Müller KE, Gaál Z, Nemes É, Felszeghy E. Health related quality of life is associated with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in overweight children. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2024;37(1):27-32. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2023-0315.
- Zhang M, Hou ZK, Huang ZB, Chen XL, Liu FB. Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Related to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systema–tic Review. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021 Apr 15;17:305-323. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S296680. PMID: 33883899; PMCID: PMC8055252.
- He Y, Duan ZJ, Wang CF, Wei YS, Cai MX. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Increases the Risk of Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022;15:199-207. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S339428.
- Didenko V, Yagmur V, Melanich S, Demeshkina L, Simonova O. Lifestyle modification in the treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A clinical case. Gastroenterologìa. 2023;56(4):252-257. https://doi.org/10.22141/2308-2097.56.4.2022.517.
- Wang Z, Zhou H, Zhang S, Wang F, Huang H. The causal relationship between COVID-19 and seventeen common digestive diseases: a two-sample, multivariable Mendelian randomization study. Hum Geno–mics. 2023 Sep 26;17(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s40246-023-00536-x. PMID: 37752570; PMCID: PMC10523605.
- Fass R, Zerbib F, Gyawali CP. AGA clinical practice update on functional heartburn: Expert review. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(8):2286-2293. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.034.
- He M, Wang Q, Yao D, Li J, Bai G. Association Between Psychosocial Disorders and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022;28(2):212-221. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm21044.
- Zamani M, Alizadeh-Tabari S, Chan WW, Talley NJ. Association Between Anxiety/Depression and Gastroesophageal Reflux: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023 Dec 1;118(12):2133-2143. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002411. Epub 2023 Jul 19. PMID: 37463429.
- Galler A, Thönnes A, Joas J, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of children, adolescents and young adults with overweight or obesity and mental health disorders. Int J Obes. 2024;48:423-432. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-023-01449-4.
- Shaqran TM, Ismaeel MM, Alnuaman A, et al. Epidemiology, Causes, and Management of Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease: A Syste–matic Review. Cureus. 2023;15(10):e47420. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47420.
- Shahnaz F, Wicaksono YS, Rahman HA. Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A Literature Review. Archives of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition. 2023;2(2):46-60. doi: 10.58427/apghn.2.2.2023.46-60.
- Rosen RD, Winters R. Physiology, Lower Esophageal Sphincter. [Updated 2023 Mar 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557452/.
- Raza D, Mohiuddin F, Khan MH, Fawad M, Raza SM. Childhood gastroesophageal reflux disease: A comprehensive review of disease, diagnosis, and therapeutic management. World J Clin Pediatr. 2025;14(2):101175 PMID: 40491743. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i2.101175.
- Antunes C, Aleem A, Curtis SA. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Archived). 2023 Jul 3. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 28722967.
- Türker SN, Barış Z, Şeker NS, Aydemir Y. Histopathological differences in pediatric duodenogastric reflux: a comparative study. Eur J Pediatr. 2025 May 14;184(6):343. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06163-z. PMID: 40369331; PMCID: PMC12078397.
- Sharma P, Yadlapati R. Pathophysiology and treatment options for gastroesophageal reflux disease: looking beyond acid. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2021 Feb;1486(1):3-14. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14501. Epub 2020 Oct 4. PMID: 33015827; PMCID: PMC9792178.
- Yang W, Huang Y, He L, et al. Utilizing Esophageal Motility Tests in Diagnosing and Evaluating Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Diagnostics. 2024;14(14):1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics1414146.
- Rosen R. Novel Advances in the Evaluation and Treatment of Children With Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Front Pediatr. 2022 Apr 1;(10):849105. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.849105. PMID: 35433543; PMCID: PMC9010502.
- Ustaoglu A, Woodland P. Sensory Phenotype of the Oesophageal Mucosa in Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023;24(3):2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032502.
- Hockley JRF, Barker KH, Taylor TS, et al. Acid and Inflammatory Sensitisation of Naked Mole-Rat Colonic Afferent Nerves. Mol. Pain. 2020;16:1744806920903150. doi: 10.1177/1744806920903150.
- Corovic I, Maksic M, Radojevic D, Vucelj S, et al. Esophageal Motility Disorders and Dysphagia: Understanding Causes and Consequences. IntechOpen. 2024. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.1006838.
- Ghamar-Shooshtari A, Rahimian Z, Poustchi H. et al. Polypharmacy and pattern of medication use among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: results from Pars Cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023;23(1):439. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-03086-7.
- Dincer BT, Urganci N, Gulec SG. Drug-induced Esophagitis as Rare Cause of Dysphagia in Adolescent Patients: Four Case Reports. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2025 Feb 7;59(2):255-257. doi: 10.14744/SEMB.2024.59196. PMID: 40756294; PMCID: PMC12314455.
- Hu S-W, Chen A-C, Wu S-F. Drug-Induced Esophageal Ulcer in Adolescent Population: Experience at a Single Medical Center in Central Taiwan. Medicina. 2021;57(12):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57121286.
- Shutova NA, Kuzmina IYu. Role of adipose tissue and adipokines in chronic inflammation development on metabolic syndrome background. International Medical Journal. 2021;1:83-87. doi: 10.37436/2308-5274-2021-15.
- Luo Y, Luo D, Li M, Tang B. Insulin Resistance in Pediatric Obesity: From Mechanisms to Treatment Strategies. Pediatr Diabetes. 2024 Jun 28;2024:2298306. doi: 10.1155/2024/2298306. PMID: 40302954; PMCID: PMC12016791.
- Wang K, Wang S, Chen Y, et al. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a genetic correlation and bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 21;15:1327503. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1327503. PMID: 38449873; PMCID: PMC10914956.
- Ciężki S, Odyjewska E, Bossowski A, Głowińska-Olszewska B. Not Only Metabolic Complications of Childhood Obesity. Nutrients. 2024 Feb 15;16(4):539. doi: 10.3390/nu16040539. PMID: 38398863; –PMCID: PMC10892374.
- Lu R, Zhou H, Yuan J, Ding Z. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and anxiety or depression: A perspective from bibliometric and visual analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 4;104(27):e43221. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043221. PMID: 40629564; PMCID: PMC12237383.
- Al-Beltagi M, Saeed NK, Bediwy AS, Elbeltagi R. Breaking the cycle: Psychological and social dimensions of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders. World J Clin Pediatr. 2025;14(2):103323. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i2.103323. PMID: 40491742.
- Kumar A, Vallabhaneni P. Anxiety disorders presenting as gastrointestinal symptoms in children — a scoping review. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025 May;68(5):344-351. doi: 10.3345/cep.2024.01732. Epub 2025 Jan 13. PMID: 39810509; PMCID: PMC12062388.
- Özenoğlu A, Anul N, Özçelikçi B. The relationship of gastroesophageal reflux with nutritional habits and mental disorders. Human Nutrition & Metabolism. 2023;33:200203. ISSN 2666-1497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hnm.2023.200203.
- Li Q, Duan H, Wang Q, et al. Analyzing the correlation between gastroesophageal reflux disease and anxiety and depression based on ordered logistic regression. Sci Rep. 2024;14:6594. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-57101-2.
- Colombo JM, Deacy AD, Schurman JV, Friesen CA. Heartburn in children and adolescents in the presence of functional dyspepsia and/or irritable bowel syndrome correlates with the presence of sleep disturbances, anxiety, and depression. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 2;100(13):e25426. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025426. PMID: 33787652; PMCID: PMC8021315.
- Бекетова Г., Мощич О., Маліновська Д., Бекетова Н., Мощич О. Особистісна та ситуативна тривожність, вегетативний статус та функціональні можливості підлітків з гастроезофагеальною рефлюксною хворобою. Східноукраїнський медичний журнал. 2025;13(2):513-525. https://doi.org/10.21272/eumj.2025;13(2):513-525.
- Bingham SM, Muniyappa P. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux disease in primary care: evaluation and care update. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2020;50(5):100784. doi: 10.1016/j.cppeds.2020.100784.
- Jaime Belkind-Gerson Gastroesophageal reflux in young children Revised/verified Sep 2023. Modified Jan 2025. https://www.msdmanuals.com/uk/professional/pediatrics/gastrointestinal-disorders-in-neonates-and-infants/gastroesophageal-reflux-in-infants.
- Durazzo M, Lupi G, Cicerchia F, et al. Extra-Esophageal Presentation of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: 2020 Update. J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 7;9(8):2559. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082559. PMID: 32784573; PMCID: PMC7465150.
- Sofokleous V, Papadopoulou AM, Giotakis E, Delides A, Kyrodimos E, et al. Pediatric Laryngopharyngeal Reflux in the Last Decade: What Is New and Where to Next? J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 10;12(4):1436. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041436. PMID: 36835970; PMCID: PMC9962831.
- Gyawali CP, Yadlapati R, Fass R, et al. Updates to the modern diagnosis of GERD: Lyon consensus 2.0. Gut. 2024;(73):361-371. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330616.
- Wu H, Li J, Li F, Lun W. Causal association of gastroesophageal reflux disease on irritable bowel syndrome: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Genet. 2024 Mar 27;15:1328327. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1328327. PMID: 38601073; PMCID: PMC11004226.
- Bai P, Bano S, Kumar S, et al. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in the Young Population and Its Correlation With Anxiety and Depression. Cureus. 2021 May 28;13(5):e15289. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15289. PMID: 34194886; PMCID: PMC8236209.
- Ahmed HAA, Yousef A, El-Kurdy R, Murad MA, Abdelwahab SM, Shiba HAA. Psychological factors, lifestyle habits, and their association with gastroesophageal reflux disease among Egyptian university students: A cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 22;103(47):e40477. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040477. PMID: 39809207; PMCID: PMC11596765.
- Jacobson JC, Pandya SR. A narrative review of gastroesophageal reflux in the pediatric patient. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jul 25;6:34. doi: 10.21037/tgh-20-245. PMID: 34423155; PMCID: PMC8343508.
- Calabrese F, Poletti V, Auriemma F, et al. New Perspectives in Endoscopic Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 14;13(12):2057. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13122057. PMID: 37370952; PMCID: PMC10297682.
- Butt I, Kasmin F. Esophageal pH Monitoring. 2023 Feb 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31971729.
- Katz PO, Dunbar KB, Schnoll-Sussman FH, Greer KB, Yadlapati R, Spechler SJ. ACG Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan 1;117(1):27-56. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001538. PMID: 34807007; PMCID: PMC8754510.
- Ahuja A, Pelton M, Raval S, Kesavarapu K. Role of Nutrition in Gastroesophageal Reflux, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Celiac Disease, and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastro Hep Advances. 2023;2(6):860-872, ISSN 2772-5723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gastha.2023.06.010.
- Lakananurak N, Pitisuttithum P, Susantitaphong P, Patcharat–rakul T, Gonlachanvit S. The Efficacy of Dietary Interventions in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Intervention Studies. Nutrients. 2024 Feb 5;16(3):464. doi: 10.3390/nu16030464. PMID: 38337748; PMCID: PMC1085732.
- Tack J, Tornblom H, Tan V, Carbone F. Evidence-Based and Emerging Dietary Approaches to Upper Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jun 1;117(6):965-972. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001780. Epub 2022 Apr 13. PMID: 35417429; PMCID: PMC9169754.
- Tosetti C, Savarino E, Benedetto E, De Bastiani R; Study Group for the Evaluation of GERD Triggering Foods. Elimination of Dietary Triggers Is Successful in Treating Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2021 May;66(5):1565-1571. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06414-z. Epub 2020 Jun 24. PMID: 32578044.
- Plaidum S, Patcharatrakul T, Promjampa W, Gonlachanvit S. The Effect of Fermentable, Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols (FODMAP) Meals on Transient Lower Esophageal Relaxations (TLESR) in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Patients with Overlapping Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Nutrients. 2022 Apr 22;14(9):1755. doi: 10.3390/nu14091755. PMID: 35565722; –PMCID: PMC9101233.
- Rivière P, Vauquelin B, Rolland E, et al. Low FODMAPs diet or usual dietary advice for the treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: An open-labeled randomized trial. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Sep;33(9):e14181. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14181. Epub 2021 May 29. PMID: 34051134.
- Mehta RS, Song M, Staller K, Chan AT. Association Between Beverage Intake and Incidence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Sep;18(10):2226-2233.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.11.040. Epub 2019 Nov 28. PMID: 31786327.
- Ketil Størdal, Carolyn E. Beck Reducing the use of proton pump inhibitors in infants with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms Canadian Family Physician March 2025;71(3):170-172. doi: https://doi.org/10.46747/cfp.7103170.
- Dipasquale V, Cicala G, Spina E, Romano C. A Narrative Review on Efficacy and Safety of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Children. Front. Pharmacol. 2022;13:839972. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.839972.
- Yibirin M, De Oliveira D, Valera R, Plitt AE, Lutgen S. Adverse Effects Associated with Proton Pump Inhibitor Use. Cureus. 2021 Jan 18;13(1):e12759. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12759. PMID: 33614352; –PMCID: PMC7887997.
- Tatsuguchi A, Hoshino S, Kawami N, et al. Influence of hypergastrinemia secondary to long-term proton pump inhibitor treatment on ECL cell tumorigenesis in human gastric mucosa. Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Oct;216(10):153113. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153113. Epub 2020 Jul 13. PMID: 32853950.
- Wang YH, Wintzell V, Ludvigsson JF, Svanström H, Pasternak B. Association Between Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and Risk of Fracture in Children. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Jun 1;174(6):543-551. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0007. PMID: 32176276; PMCID: PMC7076540.
- Savarino V, Marabotto E, Zentilin P, et al. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and pharmacological treatment of gastro-esophageal reflux disease. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;13(4):437-449. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2020.1752664. Epub 2020 Apr 17. PMID: 32253948.
- Katzka DA, Kahrilas PJ. Advances in the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. BMJ. 2020 Nov 23;371:m3786. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3786. PMID: 33229333.
- Khader Y, Abu Khudair S, Tanaka E, et al. Psychosocial, emotional and behavioral problems, quality of life, and mental health care seeking behaviors among children and adolescents in Jordan: a national school-based survey. Front. Public Health. 2024;12(12):1409158. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1409158.
- Kovács KE, Boris P, Nagy BE. Psychological Well-Being and Life Satisfaction in Children and Adolescents with Chronic Illness: The Role of Depression, Nonproductive Thoughts, and Problematic Internet Use. Children. 2025;12(5):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050657.