Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Оцінка рівнів іризину та ліпідного профілю в чоловіків з ожирінням та цукровим діабетом 2-го типу
Авторы: Duha T. Al-Taie, Muneera M. Adlan
Ministry of Education, Basrah, Iraq
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
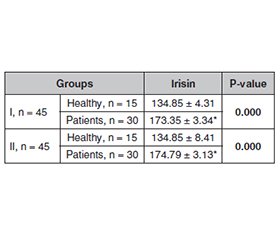
Актуальність. Цукровий діабет (ЦД) є глобальною проблемою охорони здоров’я внаслідок змін способу життя, які полягають в порушенні харчування та стилю життя, а також зниженій фізичній активності. Іризин — новий адипокін із важливими автокринними й ендокринними функціями. Він продукується не тільки м’язовою тканиною, але й лімфоїдними органами, жировою і нервовою тканиною. Мета: оцінити рівень іризину та деяких біохімічних параметрів у чоловіків з ожирінням і ЦД 2-го типу, а також визначити зв’язок іризину з показниками глікемії в чоловіків із ЦД 2-го типу й ожирінням i здорових людей. Матеріали та методи. Дослідження включало збір 90 зразків крові (60 від чоловіків із ЦД 2-го типу й ожирінням і 30 від здорових осіб), що були розділені на дві групи за віком учасників: 24–44 та 45–65 років. Кожна включала 45 зразків (30 від пацієнтів і 15 від здорових осіб). Результати. Індекс маси тіла та рівень іризину в сироватці крові хворих із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу й ожирінням в обох вікових групах були вірогідно підвищені порівняно зі здоровими учасниками (P ≤ 0,05). Концентрація глюкози в пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу й ожирінням в обох вікових групах також була вірогідно підвищена порівняно зі здоровими людьми (P ≤ 0,05). Щодо біохімічних тестів, які включали оцінку показників ліпідного профілю, то результати показали вірогідне збільшення концентрації загального холестерину, тригліцеридів, ліпопротеїнів низької та дуже низької щільності у сироватці крові пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу в обох вікових групах порівняно зі здоровими особами. Спостерігалося вірогідне зниження (P ≤ 0,05) вмісту ліпопротеїнів високої щільності в сироватці крові пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу й ожирінням в обох вікових групах порівняно зі здоровими людьми. Висновки. Рівень іризину та показники ліпідограми були підвищені в пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу та ожирінням, що свідчить про взаємозв’язок між умістом цього міокіну й порушеннями ліпідного профілю в чоловіків із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу.
Background. Diabetes mellitus (DM) represents a global health problem as a result of lifestyle changes, represented by altered dietary habits and the city life that community members live, as well as lack of movement. Irisin belongs to the class of muscle-fat kinetics because it works in both fatty and muscular tissues. It is a thermogenic protein that stimulates energy production and the burning of brown adipose tissue when exercising. The present study purposed to estimate the level of irisin hormone and some biochemical parameters in obese men with type 2 DM, and to determine the relationship of irisin with the level of blood sugar accumulation in men with type 2 DM and obesity, and in healthy people. Materials and methods. The study included collecting 90 blood samples: 60 from men with type 2 DM and obesity, and 30 from unaffected (healthy) men. The samples were divided into two groups based on age of participants: 24–44 and 45–65 years. Each of them included 45 samples (30 from patients and 15 from healthy individuals). Results. The body mass index and serum irisin level of patients with type 2 DM and obesity in both age groups were significantly increased compared to healthy subjects at the probability level of P ≤ 0.05. The results also showed that the glucose concentration and cumulative sugar of patients with type 2 DM and obesity in both age groups were significantly increased compared to healthy subjects at the probability level of P ≤ 0.05. As for the biochemical tests that included lipid profile evaluation, there was a significant increase in total cholesterol, triglycerides, low- and very low-density lipoprotein in the serum of patients with type 2 DM in both age groups compared to healthy people. The concentration of high-density lipoprotein in the serum of patients with type 2 DM and obesity in both age groups decreased significantly compared to healthy people at the probability level of P ≤ 0.05. Conclusions. The current study concluded that serum irisin levels and most lipid profile parameters were elevated in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity, which may indicate an association between the content of this myokine and lipid profile disorders in men with DM.
іризин; цукровий діабет 2-го типу; ліпідний профіль; чоловіки
irisin; type 2 diabetes mellitus; lipid profile; men
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Bahari NI, Ahmad N, Mahmud MH, Baharom M, Amir SM, Peng CS, et al. Issues and challenges in the primary prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. J Prev. 2023;44(1):105‐125. doi: 10.1007/s10935-022-00707-x.
- Cloete L. Diabetes mellitus: an overview of the types, symptoms, complications and management. Nurs Stand. 2022;37(1):61‐66. doi: 10.7748/ns.2021.e11709.
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119.
- Gregory GA, Robinson TIG, Linklater SE, Wang F, Colagiu–ri S, de Beaufort C, Donaghue KC; International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas Type 1 Diabetes in Adults Special Interest Group; Magliano DJ, Maniam J, Orchard TJ, Rai P, Ogle GD. Global incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes in 2021 with projection to 2040: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(10):741‐760. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00218-2.
- Chandrasekaran P, Weiskirchen R. The role of obesity in type 2 diabetes mellitus — an overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(3):1882. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031882.
- Ceriello A, Prattichizzo F. Variability of risk factors and diabetes complications. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021;20(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01289-4.
- Blüher M. Metabolically healthy obesity. Endocr Rev. 2020;41(3):bnaa004. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa004.
- Alnowihi SM, Al Doghaither HA, Osman NN. Serum visfatin concentration and its relationship with sex hormones in obese Saudi women. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2020;14(3):9‐13.
- Barazzoni R, Gortan Cappellari G, Ragni M, Nisoli E. Insulin resistance in obesity: an overview of fundamental alterations. Eat Weight Disord. 2018;23(2):149‐157. doi: 10.1007/s40519-018-0481-6.
- Berthoud HR, Klein S. Advances in obesity: causes, consequences, and therapy. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(7):1635‐1637. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.045.
- Vitali A, Murano I, Zingaretti MC, Frontini A, Ric–quier D, Cinti S. The adipose organ of obesity-prone C57BL/6J mice is composed of mixed white and brown adipocytes. J Lipid Res. 2012;53(4):619‐629. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M018846.
- Polyzos SA, Mathew H, Mantzoros CS. Irisin: a true, circulating hormone. Metabolism. 2015;64(12):1611‐1618. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.09.001.
- Rodríguez A, Becerril S, Ezquerro S, Méndez-Giménez L, Frühbeck G. Crosstalk between adipokines and myokines in fat browning. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017;219(2):362‐381. doi: 10.1111/apha.12686.
- Gesta S, Tseng YH, Kahn CR. Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell. 2007;131(2):242‐256. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.004.
- Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like deve–lopment of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):463-468. doi: 10.1038/nature10777.
- Shoukry A, Shalaby SM, El-Arabi Bdeer S, Mahmoud AA, Mousa MM, Khalifa A. Circulating serum irisin levels in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. IUBMB Life. 2016;68(7):544-556. doi: 10.1002/iub.1511.
- Jia J, Yu F, Wei WP, Yang P, Zhang R, Sheng Y, Shi YQ. Relationship between circulating irisin levels and overweight/obesity: a meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases. 2019;7(12):1444-1455. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i12.1444.
- Shelbaya S, Abu Shady MM, Nasr MS, Bekhet MM, Mageed YA, Abbas M. Study of irisin hormone level in type 2 diabetic patients and patients with diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018;14(5):481-486. doi: 10.2174/1573399813666170829163442.
- Gao W, Pu L, Wei J, Yao Z, Wang Y, Shi T, et al. Serum antioxidant parameters are significantly increased in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after consumption of Chinese propolis: a randomized controlled trial based on fasting serum glucose level. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9(1):101-111. doi: 10.1007/s13300-017-0341-9.
- Vetcher AA, Zhukov KV, Gasparyan BA, Shishonin AY. Hypothetical reason for the restoration of HbA1c level for pre-diabetic patients through the recovery of arterial blood flow access to rhomboid fossa. Diabetology. 2022;3(3):470-476. doi: 10.3390/diabeto–logy3030035.
- Hori M, Satoh M, Furukawa K, Sakamoto Y, Hakamata H, Komohara Y, et al. Acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-2 (ACAT-2) is responsible for elevated intestinal ACAT activity in diabetic rats. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(9):1689-1695. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000137976.88533.13.
- Nomani H, Hesami O, Vaisi-Raygani A, Tanhapour M, Bahrehmand F, Rahimi Z, et al. Association between the -11377 C/G and -11391 G/A polymorphisms of adiponectin gene and adiponectin levels with susceptibility to type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in population from the west of Iran, correlation with lipid profile. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3):3574-3582. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27634.
- Tsaryk I, Pashkovska N, Pankiv V, Pashkovskyy V. Dyslipidemia in latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: the relationship with vitamin D. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2024;20(5):357-363. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.20.5.2024.1420.
- Suryawanshi NP, Bhutey AK, Nagdeote AN, Jadhav AA, Manoorkar GS. Study of lipid peroxide and lipid profile in diabetes mellitus. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2006;21(1):126-130. doi: 10.1007/BF02913080.
- Shabana, Shahid SU, Sarwar S. The abnormal lipid profile in obesity and coronary heart disease (CHD) in Pakistani subjects. Lipids Health Dis. 2020;19(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01248-0.
- Milyani AA, Al-Agha AE. The effect of body mass index and gender on lipid profile in children and adolescents in Saudi Arabia. Ann Afr Med. 2019;18(1):42-46. doi: 10.4103/aam.aam_17_18.
- Sutter I, Velagapudi S, Othman A, Riwanto M, Manz J, Rohrer L, et al. Plasmalogens of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) are associated with coronary artery disease and anti-apoptotic activity of HDL. Atherosclerosis. 2015;241(2):539-546. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.05.037.
- Fisher EA. The degradation of apolipoprotein B100: multiple opportunities to regulate VLDL triglyceride production by different proteolytic pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1821(5):778-781. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.02.001.