Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Респіраторна підтримка при хірургічному лікуванні рубцевих стенозів трахеї на тлі тиреоїдної патології
Авторы: Бойко В.В. (1, 2), Кріцак В.В. (1, 3), Сочнєва А.Л. (1, 3), Ткаченко В.В. (1, 3)
(1) - ДУ «Інститут загальної та невідкладної хірургії імені В.Т. Зайцева НАМН України», м. Харків, Україна
(2) - Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
(3) - Навчально-науковий медичний інститут, Національний технічний університет «Харківський політехнічний інститут», м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
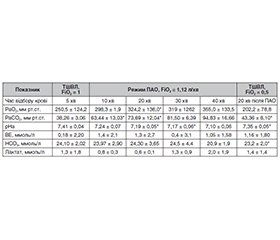
ктуальність. Останнім часом хірургічні втручання на грудній клітці та дихальних шляхах відзначилися значним прогресом. Усе більше в практику входять нові способи проведення складних резекцій та реконструкцій дихальних шляхів. Розвивається регенеративна медицина — від використання трупних трансплантатів до сучасних біосинтетичних дихальних шляхів. У зв’язку з цим необхідні знання та вміння щодо використання різних спеціальних респіраторних методик. Мета: вивчити методи респіраторної підтримки у хірургії трахеї з позицій безпеки пацієнта, хірургічного комфорту й інтраопераційної взаємодії хірурга та анестезіолога. Матеріали та методи. До дослідження було включено 130 пацієнтів зі стенозуючими захворюваннями трахеї та головних бронхів на тлі патології щитоподібної залози (ЩЗ), прооперованих у клініці Інституту з 2017 року із застосуванням потокової апноетичної оксигенації на етапах резекції та реконструкції дихальних шляхів. Середній вік пацієнтів становив 39 ± 12 років, фізичний статус за класифікацією Американського товариства анестезіологів відповідав I–II класам. Потокова апноетична оксигенація застосовувалася на основних етапах циркулярної резекції трахеї з анастомозом, трахеопластики з встановленням Т-подібної трубки, роз’єднання трахеостравохідної нориці з циркулярною резекцією трахеї, дворівневої циркулярної резекції трахеї, інших трахеопластичних операцій. Результати. Перевагами потокової апноетичної оксигенації щодо хірургічного комфорту були: знерухомлення легень та дихальних шляхів, відсутність розпилення трахеобронхіального секрету та крові з операційної рани та профілактика ускладнень, пов’язаних з порушенням прохідності дихальних шляхів, при хірургічних маніпуляціях, які можуть ускладнитися баротравмою легені. Респіраторне забезпечення операцій резекції та реконструкції дихальних шляхів у пацієнтів із захворюваннями ЩЗ може бути виконане із застосуванням потокової апноетичної оксигенації. Висновки. Методика потокової апноетичної оксигенації дозволяє уникнути серйозних ускладнень, пов’язаних із респіраторним забезпеченням, властивих іншим методикам. Вибір технології визначається рівнем та видом ураження, ступенем стенозу та протяжністю ураженої ділянки, особливостями хірургічного підходу.
Background. Currently, surgical interventions on the chest and respiratory tract have undergone significant progress. New methods of performing complex resections and reconstructions of the respiratory tract are increasingly being introduced into practice. Regenerative medicine is developing — from the use of cadaveric transplants to modern biosynthetic respiratory tracts. In this regard, knowledge and skills in using various special respiratory techniques are necessary. The purpose of the work was to study the methods of respiratory support in tracheal surgery from the standpoint of patient safety, surgical comfort and intraoperative interaction between the surgeon and anesthesiologist. Materials and methods. The study included 130 patients with stenosing diseases of trachea and main bronchi on the background of thyroid pathology who were operated on in the Institute’s clinic since 2017 using flow apnoeic oxygenation at the stages of resection and reconstruction of the respiratory tract. The average age of the patients was 39 ± 12 years, the physical status according to the classification of the American Society of Anesthesiologists corresponded to classes I–II. Flow apnoeic oxygenation was used at the main stages of circular tracheal resection with anastomosis, tracheoplasty with the placement of a T-shaped tube, separation of the tracheoesophageal fistula with circular tracheal resection, two-level circular tracheal resection, and other tracheoplastic operations. Results. The advantages of flow apnoeic oxygenation in terms of surgical comfort were immobility of the lungs and airways, absence of spraying of tracheobronchial secretions and blood from the surgical wound, and prevention of complications associated with impaired airway patency during surgical manipulations, which can be complicated by lung barotrauma. Respiratory support for resection and reconstruction of the airways in patients with thyroid diseases can be performed using flow apnoeic oxygenation. Conclusions. The flow apnoeic oxygenation technique allows avoiding serious complications associated with respiratory support inherent in other techniques. The choice of technology is determined by the level and type of lesion, the degree of stenosis, the length of the affected area, and the characteristics of the surgical approach.
стенозуючі захворювання трахеї; захворювання щитоподібної залози; резекції та реконструкції дихальних шляхів; респіраторне забезпечення
stenosing diseases of the trachea; thyroid diseases; resection and reconstruction of the respiratory tract; respiratory support
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Dalar L, Karasulu L, Abul Y, Özdemir C, Sökücü SN, Tarhan M, Altin S. Bronchoscopic Treatment in the Management of Benign Tracheal Stenosis: Choices for Simple and Complex Tracheal Stenosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016 Apr;101(4):1310-7. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Dec 17. PMID: 26704411.
- Ezemba N, Echieh CP, Chime EN, Okorie CO, Okonna FG, Idoko FL, Arua OA. Postintubation tracheal stenosis: Surgical mana–gement. Niger J Clin Pract. 2019 Jan;22(1):134-137. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_288_18. PMID: 30666033.
- Freitas C, Martins N, Novais-Bastos H, Morais A, Fernan–des G, Magalhães A. The role of interventional bronchoscopy in the management of post-intubation tracheal stenosis: A 20-year experience. Pulmonology. 2021 Jul-Aug;27(4):296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2019.12.004. Epub 2019 Dec 31. PMID: 31901372.
- Ito T, Shingu K, Maeda C, Kitazawa M, Mizukami Y, Hiraguri M, Horigome N, et al. Acute airway obstruction due to benign asymptomatic nodular goiter in the cervical region: A case report. Oncol Lett. 2015 Sep;10(3):1453-1455. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3464. Epub 2015 Jul 8. PMID: 26622689; PMCID: PMC4533311.
- Liu J, Wu W, Liu S, Xu Z, Wang J, Li B. A Modified Tracheal Transaction Approach for the Repair of Nonmalignant Tracheoesopha–geal Fistulas: A Report of 5 Cases. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2017;79(3):147-152. doi: 10.1159/000468943. Epub 2017 Apr 8. PMID: 28391268.
- Murgu SD, Egressy K, Laxmanan B, Doblare G, Ortiz-Comi–no R, Hogarth DK. Central Airway Obstruction: Benign Strictures, Tracheobronchomalacia, and Malignancy-related Obstruction. Chest. 2016 Aug;150(2):426-41. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 11. PMID: 26874192.
- Qureshi YA, Muntzer Mughal M, Markar SR, Mohammadi B, George J, Hayward M, Lawrence D. The surgical management of non-malignant aerodigestive fistula. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018 Nov 15;13(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13019-018-0799-1. PMID: 30442164; PMCID: PMC6238307.
- Zuo T, Gao Z, Chen Z, Wen B, Chen B, Zhang Z. Surgical Management of 48 Patients with Retrosternal Goiter and Tracheal Stenosis: A Retrospective Clinical Study from a Single Surgical Center. Med Sci Monit. 2022 Aug 11;28:e936637. doi: 10.12659/MSM.936637. PMID: 35949114; PMCID: PMC9380444.
- Xiong XF, Xu L, Fan LL, Cheng DY, Zheng BX. Long-term follow-up of self-expandable metallic stents in benign tracheobronchial stenosis: a retrospective study. BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Feb 8;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-0793-y. PMID: 30736856; PMCID: PMC6368722.
- Jin S, Sugitani I. Narrative review of management of thyroid surgery complications. Gland Surg. 2021 Mar;10(3):1135-1146. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-859. PMID: 33842257; PMCID: PMC8033047.
- Misaki M, Kawakita N, Hara T, Yamagami H, Takeuchi T, Miyamoto N, Sakamoto S, et al. Silicone stent placement for tracheal stenosis induced by a giant goiter due to Graves’ disease: a case report. Gland Surg. 2024 Apr 29;13(4):578-583. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-499. Epub 2024 Apr 17. PMID: 38720672; PMCID: PMC11074657.
- Kim WK, Shin JH, Kim JH, Song JW, Song HY. Management of tracheal obstruction caused by benign or malignant thyroid disease using covered retrievable self-expandable nitinol stents. Acta Radiol. 2010 Sep;51(7):768-74. doi: 10.3109/02841851.2010.491093. PMID: 20707660.
- Kather D, Steinack C, Franzen DP. Endoscopic treatment of benign tracheal stenosis: a single-centre study. Swiss Med Wkly. 2024 Jun 17;154:3363. doi: 10.57187/s.3363. PMID: 38885613.
- Marchioni A, Andrisani D, Tonelli R, Andreani A, Cappiello GF, Ori M, et al. Stenting versus balloon dilatation in patients with tracheal benign stenosis: The STROBE trial. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022;7(2):395-403. Epub 2022 Apr 19. doi: 10.1002/lio2.734. PubMed PMID: 35434321; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC9008152.
- Ravikumar N, Ho E, Wagh A, Murgu S. The role of bronchoscopy in the multidisciplinary approach to benign tracheal stenosis. J Thorac Dis. 2023;15(7):3998-4015. Epub 2023 Aug 10. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1734. PubMed PMID: 37559626; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC10407490.
- Auchincloss HG, Wright CD. Complications after tra–cheal resection and reconstruction: prevention and treatment. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8(Suppl 2):S160-7. Epub 2016 Mar 17. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2016.01.86. PubMed PMID: 26981267; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4775259.
- Lukinović J, Bilić M. Overview of Thyroid Surgery Complications. Acta Clin Croat. 2020 Jun;59(Suppl 1):81-86. doi: 10.20471/acc.2020.59.s1.10. PMID: 34219888; PMCID: PMC8212606.
- Mishra T, Mohapatra I, Srivastava V, Rout TK. Assessment of Post-operative Complications in Patients Undergoing Thyroid Surgery in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Eastern India. Cureus. 2023 Jul 27;15(7):e42549. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42549. PMID: 37637525; PMCID: PMC10460142.
- Pankiv V. Coexistence of accompanying autoimmune diseases in adolescents with autoimmune thyroiditis. Child’s Health. 2024;19(7):429-433. https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0551.19.7.2024.1754.
- Kamyshna I, Pavlovych L, Pankiv V, Khodorovska A, Bilous O, Kamyshnyi O. The molecular fundamentals of neurorehabilitation and their modulation by thyroid hormones. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2024;20(2):126-132. https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0721.20.2.2024.1374.