Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 59, №2, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Eфективність застосування ліраглутиду в пацієнтів із метаболічно асоційованою стеатотичною хворобою печінки при цукровому діабеті 2 типу
Авторы: Yu.M. Stepanov (1), O.V. Zinych (2), I.A. Klenina (1), K.O. Shyshkan-Shyshova (2), N.M. Kushnarоva (2)
(1) - Institute of Gastroenterology of NAMSU, Dnipro, Ukraine
(2) - V.P. Komisarenko Institute of Endocrinology and Metabolism of NAMSU, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
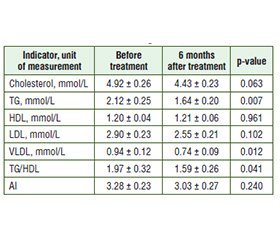
Актуальність. Зростання захворюваності на метаболічно асоційовану стеатотичну хворобу печінки (МАСХП) та цукровий діабет (ЦД) 2 типу спонукає лікарів до вдосконалення стратегій діагностики, профілактики і терапії цих метаболічних станів. Мета: дослідити вплив агоністів рецепторів глюкагоноподібного пептиду-1 (арГПП-1) на вираженість метаболічних порушень у пацієнтів із МАСХП та ЦД 2 типу в динаміці лікування. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження було включено 30 пацієнтів віком (56,5 ± 7,8) року із МАСХП та ЦД 2 типу. Їм призначали арГПП-1 ліраглутид із поступовою титрацією до максимальної дози. Для оцінки композиційного складу тіла використовували ваги-аналізатори TANITA BC-545N (Японія). У сироватці крові визначали рівень глюкози, глікозильованого гемоглобіну (HbA1c), показники ліпідного та вуглеводного обміну. Коефіцієнт атерогенності розраховували за формулою W.T. Friedewald, на підставі даних біоімпедансометрії, а також ліпідного і вуглеводного обміну розраховували індекси TyG, TyG-BMI, TyG-WC. Статистичну обробку результатів дослідження здійснювали за допомогою методів варіаційної статистики з використанням програмного пакета StatSoft Statistica 10.0. Результати. Після лікування арГПП-1 встановлено вірогідне зниження рівня глюкози в сироватці крові до фізіологічної норми у 26,7 % пацієнтів та HbA1c — у 66,7 %. Терапія сприяла зменшенню індексу маси тіла у 28 (93,3 %) із 30 пацієнтів, відсотка жиру — у 25 (83,3 %), кількість випадків вісцерального ожиріння знизилася до 17 (56,7 %). Застосування арГПП-1 приводило до позитивної динаміки у вигляді зменшення рівня тригліцеридів у сироватці крові в 1,3 раза — (1,64 ± 0,20) ммоль/л проти (2,12 ± 0,25) ммоль/л до лікування. Рівень холестерину, який був підвищений в 11 пацієнтів, після терапії знизився у 6 випадках. Використання ліраглутиду обумовило зменшення індексів TyG, TyG-BMI, TyG-WC. Висновки. У пацієнтів із МАСХП та ЦД 2 типу лікування ліраглутидом протягом 6 місяців сприяло зниженню вмісту жирової тканини та позитивній динаміці показників вуглеводного й ліпідного обміну. Визначення індексу TyG є корисним для оцінки інсулінорезистентності, індекси TyG-BMI, TyG-WC рекомендовано використовувати як доступну альтернативу для моніторингу ефективності лікування.
Background. The increasing incidence of metabolism-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and type 2 diabetes prompts physicians to improve strategies for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of these metabolic conditions. Objective: to investigate the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (arGLP-1) on the severity of metabolic disorders in patients with MASLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the dynamics of treatment. Materials and methods. The study included 30 patients aged (56.5 ± 7.8) years with MASLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus. They were prescribed liraglutide, a arGLP-1, with gradual titration to the maximum dose. To assess body composition, body composition analyzers TANITA BC-545N (Japan) were used. Serum levels of glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), parameters of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism were determined. The atherogenic index was calculated according to the formula of W.T. Friedewald, the TyG, TyG-BMI, TyG-WC indices were calculated based on the obtained bioimpedance analysis data, as well as lipid and carbohydrate metabolism indicators. Statistical processing of the study results was carried out by methods of variation statistics using the software package StatSoft Statistica 10.0. Results. After treatment with arGLP-1, a significant decrease in serum glucose to physiological norm was observed in 26.7 % of patients, and a reduction in HbA1c levels — in 66.7 %. The therapy led to a reduction in body mass index in 28 (93.3 %) of 30 patients, in body fat percentage — in 25 (83.3 %), and the number of cases of visceral obesity decreased to 17 (56.7 %). After the use of arGLP-1, a positive trend was observed in the form of a 1.3-fold decrease in serum triglyceride levels to (1.64 ± 0.20) mmol/L versus (2.12 ± 0.25) mmol/L before treatment. Serum cholesterol, which was elevated in 11 patients, reduced in 6 cases after therapy. The use of liraglutide led to a reduction in the TyG, TyG-BMI, TyG-WC indices. Conclusions. In patients with MASLD and type 2 diabetes, treatment with liraglutide for 6 months contributed to a decrease in the amount of fat in body composition and a positive dynamics of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. The determination of the TyG index is a useful indicator for assessing insulin resistance, and the TyG-BMI and TyG-WC indices are recommended to be used as an affordable alternative for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
метаболічно асоційована стеатотична хвороба печінки; цукровий діабет 2 типу; агоністи рецепторів глюкагоноподібного пептиду-1; вісцеральний жир
metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease; type 2 diabetes mellitus; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; visceral fat
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Stepanov YuM, Didenko VI, Klenina IA, Tatarchuk OM, Petishko OP. Improving the verification of liver fibrosis using new minimally invasive markers in patients with chronic diffuse liver diseases. Med Perspect. 2022;27(4):100-114. doi: 10.26641/2307-0404.2022.4.271181 (in Ukrainian).
- Didenko V, Klenina I, Tatarchuk O, Petishko O. Correlation of immunological and biochemical parameters in patients with chronic diffuse liver diseases depending on the etiological factors of liver steatosis and fibrosis. Gastroenterol. 2021;53(2):115-122. doi: 10.22141/2308-2097.53.2.2019.168985.
- Lee CH, Lui DT, Lam KS. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: An update. J Diabetes Investig. 2022;13(6):930-940. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13756.
- Frankowski R, Kobierecki M, Wittczak A, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and metabolic repercussions: The vicious cycle and its interplay with inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(11):9677. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119677.
- Zheng D, Cai J, Xu S, Jiang S, Li C, Wang B. The associa–tion of triglyceride-glucose index and combined obesity indicators with chest pain and risk of cardiovascular disease in American popu–lation with pre-diabetes or diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1471535. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1471535.
- Dang K, Wang X, Hu J, et al. The association between triglyceride-glucose index and its combination with obesity indicators and cardiovascular disease: NHANES 2003–2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024;23(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02115-9.
- Selvi NMK, Nandhini S, Sakthivadivel V, Lokesh S, Sriniva–san AR, Sumathi S. Association of triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) with HbA1c and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Maedica (Bucur). 2021;16(3):375-381. doi: 10.26574/maedica.2021.16.3.375.
- Ferguson D, Finck BN. Emerging therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(8):484-495. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00507-z.
- Lee HA, Kim HY. Therapeutic mechanisms and clinical effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(11):9324. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119324.
- Guo T, Yan W, Cui X, et al. Liraglutide attenuates type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating AMPK/ACC signaling and inhibiting ferroptosis. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00721-7.
- Rochon J, Kalinowski P, Szymanek-Majchrzak K, Grąt M. Role of gut-liver axis and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2024;30(23):2964-2980. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i23.2964.
- Wilbon SS, Kolonin MG. GLP1 receptor agonists-effects beyond obesity and diabetes. Cells. 2023;13(1):65. doi: 10.3390/cells13010065.
- Nauck MA, Quast DR, Wefers J, Meier JJ. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes — state-of-the-art. Mol Metab. 2021;46:101102. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101102.
- Mao ZH, Gao ZX, Liu DW, Liu ZS, Wu P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites — molecular mechanisms and management strategies in diabetic kidney disease. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1124704. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1124704.
- Younossi ZM, Golabi P, Price JK, et al. The global epidemio–logy of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22(10):1999-2010.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.03.006.
- Ferdous SE, Ferrell JM. Pathophysiological relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: novel therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(16):8731. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168731.
- Semmler G, Balcar L, Wernly S, et al. Insulin resistance and central obesity determine hepatic steatosis and explain cardiovascular risk in steatotic liver disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1244405. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1244405.
- Laeeq T, Tun KM. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cardiovascular disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2024;23(1):e0181. doi: 10.1097/CLD.0000000000000181.
- Pan Y, Zhao M, Song T, et al. Role of triglyceride-glucose index in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024;17:3325-3333. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S478287.
- Ramdas Nayak VK, Satheesh P, Shenoy MT, Kalra S. Triglyceride glucose (TyG) index: a surrogate biomarker of insulin resistance. J Pak Med Assoc. 2022;72(5):986-988. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.22-63.
- Muzurović EM, Volčanšek Š, Tomšić KZ, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of obesity/metabolic syndrome, prediabetes/diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease — current evidence. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2022;27:10742484221146371. doi: 10.1177/10742484221146371.
- Isaacs SD, Farrelly FV, Brennan PN. Role of anti-diabetic medications in the management of MASLD. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2025;16:239-249. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2024-102856.
- Meneses MJ, Patarrão RS, Pinheiro T, et al. Leveraging the future of diagnosis and management of diabetes: from old indexes to new technologies. Eur J Clin Invest. 2023;53(4):e13934. doi: 10.1111/eci.13934.