Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 19, №7, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Оцінка рівня кальцію, магнію та цинку в сироватці крові хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го типу в українській популяції
Авторы: V.І. Kravchenko (1), K.Yu. Ivaskiva (1), I.M. Andrusyshyna (2), V.I. Pankiv (3), M.D. Khalangot (1), V.L. Orlenko (1), V.L. Vasiuk (4)
(1) — State Institution “V.P. Komisarenko Institute of Endocrinology and Metabolism of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine”, Kyiv, Ukraine
(2) — State Institution “Kundiiev Institute of Occupational Health of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
(3) — Ukrainian Research and Practical Centre for Endocrine Surgery, Transplantation of Endocrine Organs and Tissues of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
(4) — Bukovinian State Medical University, Chernivtsi, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
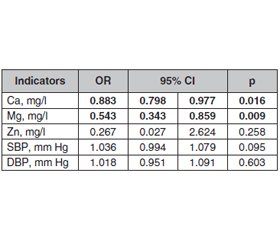
Актуальність. Дослідження присвячене вивченню вмісту кальцію, магнію і цинку в осіб із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу (ЦД2). Мета: встановити рівень кальцію, магнію та цинку в сироватці крові хворих на ЦД 2-го типу. Матеріали та методи. Відкрите контрольоване дослідження включало 27 пацієнтів із ЦД2. Контрольну групу становили 12 осіб без ендокринних та соматичних захворювань. У 70 % хворих діабет виявлено вперше, у інших тривалість захворювання була до п’яти років. Cередній вік обстежених становив 61,83 ± 5,52 року для пацієнтів з ЦД2 та 55,25 ± 5,52 року для контрольної групи. У групі ЦД2 жінок було 62,96 %, у контрольній — 63,64 %. Антропометричні вимірювання та визначення показників глюкози проводили за стандартною методикою. Концентрації кальцію, магнію, цинку в сироватці крові оцінювали за допомогою атомно-оптичної емісійної спектрометрії з індуктивно-зв’язаною плазмою (модель PerkinElmer Optima 2100 DV ICP-OES, США) згідно з оригінальною методикою, затвердженою Інститутом медицини праці ім. І.Ю. Кундієва НАМН України. Результати. Рівень цукру натще в сироватці крові пацієнтів перебував в межах від 7,1 до 17,2 ммоль/л і вказував на наявність ЦД2, уміст глікованого гемоглобіну становив від 7,1 до 11,2 %. За антропометричними даними група хворих повністю відповідала групі контролю. Хоча вже на стадії початкового діабету було зареєстровано незначне збільшення маси тіла та окружності талії, рівень тригліцеридів вірогідно виріс, а вміст холестерину ліпопротеїнів високої щільності зменшився. Установлено вірогідне зниження рівня кальцію та магнію в сироватці крові хворих на ЦД2. Уміст цинку в крові перебував на рівні нижньої межі референтного значення в 44 % пацієнтів та лише в 16,6 % осіб у контрольній групі. Вірогідних відмінностей за цим показником у групах спостереження не було. Виявлено високий кореляційний зв’язок між досліджуваними показниками в крові, а також зворотний зв’язок між рівнем глюкози натще та вмістом кальцію і магнію. Висновки. Виявлено вірогідне зниження рівня кальцію та магнію в крові хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го типу в українській популяції. Існує висока кореляція між рівнями кальцію, магнію та цинку в крові осіб із ЦД 2-го типу. Значний ризик розвитку діабету відзначався при зниженні концентрації кальцію та магнію в сироватці крові.
Background. The research deals with the provision of calcium, magnesium and zinc in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The purpose was to investigate the serum content of calcium, magnesium and zinc in patients with type 2 DM. Materials and methods. The open-label controlled study included 27 patients with T2DM. The control group consisted of 12 people without endocrine and somatic diseases. 70 % of patients had newly diagnosed DM; in others, the disease duration was up to 5 years. Most of the examined were of mature age, on average 61.83 ± 5.52 years for patients and 55.25 ± 5.52 years for controls. In the group with T2DM, women accounted for 62.96 %, among controls — 63.64 %. Anthropometric measurements and glucose indicators were determined according to a standard procedure. Concentrations of calcium, magnesium, zinc in serum were evaluated by atomic optical emission spectrometry with inductively coupled plasma (PerkinElmer Optima 2100 DV ICP-OES, USA) according to the original procedure approved by the Kundiiev Institute of Occupational Health of the NAMS of Ukraine. Results. The level of fasting blood sugar ranged from 7.1 to 17.2 mmol/l and indicated the presence of T2DM, glycated hemoglobin was from 7.1 to 11.2 %. According to anthropometric data, the group of patients almost completely corresponded to the control group. Although a slight increase in body weight and waist circumference was registered already at the stage of initial diabetes, the level of triglycerides increased significantly, and the level of high-density lipoprotein decreased. A significant reduction in the levels of calcium and magnesium in the blood serum of patients with T2DM was found. The zinc content was at the level of the lower edge of the reference value in 44 % of patients, in the control group — only in 16.6 % of cases. There were no significant differences in this indicator in the observation groups. A high correlation was found between the studied parameters in the blood, as well as an inverse correlation between the fasting glucose level and the content of calcium and magnesium. Conclusions. A significant decrease in the level of calcium and magnesium in the blood of Ukrainian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus was found. There is a high correlation between serum calcium, magnesium and zinc levels in patients with T2DM. Significant risks of diabetes were revealed when the serum concentration of calcium and magnesium decreased.
цукровий діабет 2-го типу; рівень глюкози в крові натще; кальцій, магній; цинк; кореляційний аналіз
type 2 diabetes mellitus; fasting blood glucose; calcium, magnesium; zinc; correlation analysis