Introduction
Recently, in most countries of the world, there is a significant increase in allergic skin diseases — allergodermatoses, especially in children. Analysis of clinical cases helps identify problems, and plan future studies, which can change the understanding of disease consequences.
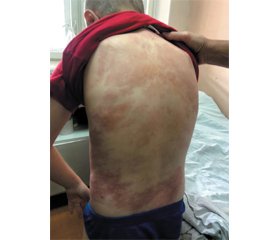
Clinical case. A 9-year-old boy was urgently admitted to the Ternopil Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital with complaints of an increase in body temperature to subfebrile numbers, itching, rashes on the skin of the back, and scratches on the upper and lower limbs.
Medical history. The patient has been sick for the past 2 weeks when the above complaints appeared and hospitalized in Chortkiv Central Hospital.
History of life: from the first pregnancy and the first childbirth. The child was not sick during the newborn period. Previous diseases: acute respiratory infection under the age of one year.
Allergic anamnesis: not aggravated. Hereditary history: not burdened. Preventive vaccinations: not received according to age. History: during last 21 days, no bowel disorders were detected. There were bedbug bites in the apartment where the child lives.
Objective status. General condition of the child was of medium severity due to intoxication syndrome. Consciousness is clear. The skin is pale, with a rash with scratches and bloody crusts. Subcutaneous adipose tissue is satisfactorily developed. Breathing through the nose is difficult. Visible mucous membranes are pale pink, and clean. Throat — moderate hyperemia. The tongue has gray coating on it. Lymph nodes are not enlarged.
Percussion limits of relative cardiac dullness are not common. Auscultatively, the activity of the heart is rhythmic, tones are sonorous. Heart rate — 98 bpm, BH — 20, body temperature — 37 °C. Auxiliary muscles do not participate in the act of breathing. Pulmonary sound percussively over the lungs. Vesicular breathing over the lungs by auscultation. The abdomen is not painful during superficial palpation. Liver +1.5 cm, is not painful, the edge is rounded. The spleen is not enlarged.
Status localis. Complaints about the appearance of rashes on the child’s back, arms, and legs, an increase in body temperature to febrile numbers. The skin is pale with traces of scratches on the hands and feet. In the lumbar region, there is a confluent maculopapular rash.
General blood test upon admission revealed leukocytosis with neutrophilia (Table 1). In the immunogram, an increase in immunoglobulin E to 600 IU/ml was observed (with reference standards < 90.0 IU/ml).
Coprogram (06.09.21): the stool is loose, dark brown, mushy, with remains of undigested food. Muscle fibers are not changed, 3–4 in the field of view. Significant amount of plant fibers is not digested. A moderate amount of mucus is detected. There is not much soap, no fatty acids; epithelial cells — 0–1 in the field of view. Leukocytes — 1–2 in the field of view, erythrocytes — 0–1.
Ther was moderate amount of fungi elements; helminth eggs were not found. A scraping for enterobiasis (02.09) — negative. General analysis of urine was without pathological changes.
Dermatologist consultation (09.02.21). The skin and mucous membranes of the oral cavity were examined. Diagnosis: toxicoderma of the skin of the back and lumbar region, maculopapular form, draining of medium severity.
Recommendations: continue treatment according to medical prescriptions. Topical emollients with constitutionally dry skin and monitoring of this rash.
Clinical diagnosis: toxicoderma, maculopapular form, draining of medium severity.
Treatment was carried out with loratadine, enterosgel, infusion therapy, and local emulsifiers.
The boy was discharged home with improvement.
Discussion
Most cases of toxicoderma proceed by the mechanism of an immediate allergic reaction after acquired sensitization of the body or in connection with idiosyncrasy (congenital intolerance). At the same time, unlike allergic contact dermatitis, the toxicoderma factor does not contact with the patient’s skin. Allergic contact dermatitis is a cell-mediated hypersensitivity reaction of the skin and is usually induced by a non-viral factor or xenobiotic (hapten) that is absorbed into the skin and reacts with self-proteins, leading to an immune response [1, 2].
The pathogenesis of toxicoderma simultaneously combines toxic and allergic components, which causes the development of various lesions on the skin, mucous membranes, vascular system, and internal organs [3].
Entering the body in various ways, a toxin is absorbed into the blood and blood vessels and reaches the skin. The basis of toxiderma pathogenesis is an allergic reaction as a manifestation of the sensitizing effect of an exogenous substance (allergen). Thus, with toxicoderma, the action of the allergen on the skin occurs as if from inside the body. As a result of the emergence, modern dermatology distinguishes 4 etiological groups of toxicodermas: medicinal, alimentary, professional, and autotoxic.
Symptoms of toxicoderma
The clinical picture is characterized by a wide variety of forms. Rashes on the skin can be papular, vesicular, erythematous, urticarial, and papulo-vesicular. Damage to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and lips can be vesicular-erosive, catarrhal, or hemorrhagic. In some cases of toxicoderma, not only the mucous membrane of the mouth is affected, but also the mucous membrane of the genitals, urethra, and anal region of the rectum. Rashes on the skin and mucous membranes in toxicoderma are usually accompanied by various subjective sensations of the patient: tension, burning, soreness, and itching of the skin in the affected areas. The basis for establishing a diagnosis of toxicoderma is its characteristic clinical picture.
/35.jpg)
Depending on the prevalence of clinical manifestations, fixed and widespread forms of toxicoderma are distinguished. A fixed form of toxicoderma in most cases is manifested by the appearance on the skin of several round erythematous spots with a diameter of 2–3 cm. Over time, the spots may acquire a brown color, and bubbles form in the middle of some of them. Elimination of the further entry of the allergen into the body leads to the disappearance of a fixed toxicoderma within 10 days.
Diagnostic algorithm
1. History collection is aimed at identifying the causative factor of the disease. In case of toxicoderma, skin allergy tests often do not give results. The use of provocative samples with a possible allergen is associated with the risk of developing a severe form of toxicoderma [4].
Skin prick tests and determination of specific IgE antibodies are used to diagnose IgE-mediated allergy of the immediate type, which mainly causes symptoms from the respiratory tract. These tests are rarely indicated for the diagnosis of skin diseases (e.g., contact urticaria, severe atopic dermatitis in young children, and food allergies).
Skin (patch) tests are used to diagnose delayed contact allergy (allergic contact dermatitis).
2. Only in vitro tests can be used to determine the causative substance: the reaction of degranulation of basophils, blast transformation of lymphocytes, agglomeration of leukocytes, and others.
3. To rule out the infectious nature of the rashes, bacteriological examination of the material, skin scrapings for pathogenic fungi, microscopy of smears for pale treponema, rapid plasma reagin test for syphilis should be performed.
4. In case of a widespread form of toxicoderma, a coagulogram and a study of the main biochemical parameters in the blood and urine analysis are performed. In case of damage to internal organs, consultation with a cardiologist, gastroenterologist, nephrologist may be necessary.
5. Electrocardiography, echoencephalography, ultrasound of abdominal organs and liver, ultrasound or computed tomography of kidneys were carried out.
6. Specific IgE antibodies were determined similarly to spot tests in the study of immediate (IgE-mediated) allergy. The level of specific antibodies to allergens is measured in the blood serum of patients. It is possible to perform group tests (usually as a screening) containing several allergens (for example, a group of allergens from dust), or to determine antibodies to individual allergens.
The clinical classification of toxicoderma according to the etiological factor distinguishes medicinal, vaccine, food, autointoxication forms, three degrees of severity (mild, moderate, severe), and the prevalence of rashes (localized, widespread, diffuse). According to the morphological elements of rashes, toxicoderma can be spotted, papular, maculopapular, urticarial, vesicular, bullous, nodular, pigmented, purpuric, bullous-hemorrhagic [2].
The diagnosis of toxicoderma is based on typical clinical criteria (rash on the skin, itching, peeling, burning, soreness of the skin of the affected areas, lacrimation, gastrointestinal disorders, fever, malaise, joint pain and headache, numbness of the tongue, pressing pain behind the sternum, palpitations, weakness, bronchospasm, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea), history data (prescription of drugs the day before, presence of similar symptoms earlier after taking drugs, history of severe allergy, effectiveness of previous desensitizing therapy), results of physical examination (characteristic skin lesions with polymorphic elements of the rash — spots, erythema, papules, blisters, knots, vesicles, bullae, erosions, hemorrhagies, which are accompanied by many unpleasant phenomena: increased body temperature, headache, general malaise, nausea, loss of appetite) [3–5], which were observed in our patient in the given clinical case. The blood analysis revealed leukocytosis, eosinophilia, accelerated ESR, hypercoagulation according to coagulogram data, increased levels of IgE and circulating immune complexes. To identify the etiological factor, specific allergological tests in vivo and in vitro are used [4]. Children with allergic dermatoses have disorders of the cellular immunity with the development of an imbalance between individual subpopulations of lymphocytes: a decrease in CD3 with an increase in CD4 and a decrease in CD8, a corresponding increase in the immunoregulatory index, as well elevated blood levels of CD20, CD19, and CD16 [7].
To the best of our knowledge, the treatment of toxicoderma primarily consists in stopping the entry into the patient’s body of all substances that could cause the disease as an etiological factor [8]. Signs and symptoms of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis were significantly reduced with baricitinib 4 mg on top of topical corticosteroids [9].
The diet is strictly hypoallergenic. Pathogenetic therapy: systemic glucocorticoids (prednisone, methylprednisolone, dexamethasone), antihistamines (loratadine, desloratadine, cetirizine, levocetirizine, chloropyramine, dimetindene), mast cell stabilizers (ketotifen, zaditen), enterosorbents (silicon dioxide, coal), detoxification therapy (glucose-saline solutions, sodium thiosulfate). Local therapy of the affected skin includes the use of topical glucocorticoids (clobetasol, betamethasone, methylprednisone, mometasone, triamcinolone, prednisone, hydrocortisone, desonide), adsorbents (zinc paste), combined preparations of a topical glucocorticoid with an antibiotic, an antifungal agent (betamethasone, gentamicin, clotrimazole) [10].
Here, we presented an unusual case of toxicoderma in a child following a bugbite complicated by allergic contact dermatitis. The treating physician needs to be alert to establish the correct diagnosis of toxic dermatitis, identify a toxic agent, stop its influence and treat the adverse reaction, usually with antihistamine and corticosteroid drugs that help stabilize the child’s condition, will contribute to the rapid regression of exanthema with enanthema and decrease the development of complications [11].
Conclusions
The peculiarity of the presented case is toxicoderma in a child after a bugbite. We study this case in order to increase the level of knowledge about the correct diagnostic algorithm. It is important to establish the correct diagnosis of toxic dermatitis, identify a toxic agent, stop its exposure and treat the adverse reaction, usually with antihistamines and corticosteroids.
Received 01.07.2022
Revised 14.07.2022
Accepted 23.07.2022
/35.jpg)

/34.jpg)
/35_2.jpg)