Международный неврологический журнал 4 (74) 2015
Вернуться к номеру
The influence of differential therapeutic approach on bioelectrical activity of a brain for patients with Parkinson''s disease and vascular encephalopathy with parcinsonian syndrome
Авторы: Cherny T.V.
Рубрики: Неврология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
The pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease is a drastic reduction content of dopamine in the substantia nigra and the striatum. Death of dopaminergic neurons is due to excessive formation of protein molecules with impaired organization - a-synuclein protein. According to many authors, the activity of various neurotransmitter systems meets certain EEG bands, such as cholinergic activity characteristic EEG activity was 6-8 Hz, for dopaminergic system - 11-12 Hz.
Aim of this study was to investigate the clinical, neurological and neurophysiological features of Parkinson's disease and vascular encephalopathy with parcinsonian syndrome.
Material and methods. Were analyzed hospital records of 22 patients aged 43 to 78 years, including 9 men and 13 women who received advice to DRK TMS. Group 1 consisted of seven patients with a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. Group 2 included 15 patients with a diagnosis of encephalopathy with parcinsonian syndrome. In clinical-neurological examination were used: Hoehn and Yahr Rating Scale, a unified Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale, MMSE, Schwab and England Scale, BDI, PDQ-39. Registration brains biopotential was performed by using neurophysiological complex DX-NT32. To assess the level of activity of the cholinergic system of the brain was determined in terms of absolute spectral power in the range of 6-7,5 Hz, dopaminergic -11-12 Hz. CNS reactivity evaluated by the change (%) of the absolute range of power and integral coefficients in response to the introduction of drugs based on the classification of types of reactions CNS. All the data were processed using statistical techniques using correlation analysis.
Results and discussion. To determine the severity of movement disorders was used classification Hoehn and Yahr Rating Scale. In the first group noted 14,3% of patients with stage I, 57,1% - from II and 28,6% -with stage III. In the second group, all patients comply with movement disorders stage II. Significant differences in gender distribution in the groups have been identified. Age-specific groups were significantly different (W-Wilcoxon test). In the first group of patients were younger (Me (± 95%) = 59 (47-69)) than in the second (Me (± 95%) = 72 (61-75)).
The initial values of the absolute spectral power in the range of 6-8 Hz, characterizing the activity of the cholinergic system in the CNS, patients first group were significantly lower (W- Wilcoxon test p ≤ 0,05), than patients of the 2nd group in the left frontal and occipital bilaterally in the cortex of the cerebral hemispheres. Baseline levels of AFM in the range of 11-12 Hz, which characterizes the dopaminergic system, leads in all investigated patients in both groups were not significant differences were reduced and (W- Wilcoxon test p ≤ 0,05) on the indicators in the control group of healthy volunteers.
Conclusions.
1. Patients of the first group (Parkinson's disease) were younger than patients of the second group (encephalopathy).
2. More pronounced CNS cholinergic system failure was detected in patients with Parkinson's disease.
3. EEG indicators that characterize the activity of dopaminergic system were reduced in both groups.
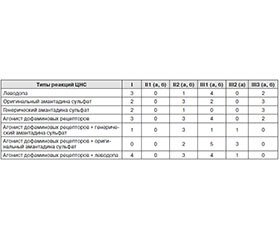
4. Features neurotransmitter deficiency predetermined destination complexes pathogenetic therapy.
5. Parkinson's disease is a necessary and effective designation of a glutamate receptor blockers(original amantadine sulphate).
6. Patients in both groups show the use a selective dopamine receptor agonists and any kind of levodopa.
7. Inclusion in the therapy of Parkinson's disease (group 1) and vascular encephalopathy with parkinsonian syndrome (group 2) complexes drugs selective dopamine receptor agonists + original amantadine sulphate, selective dopamine receptor agonists +levodopa, increases the proportion of favorable reactions CNS.